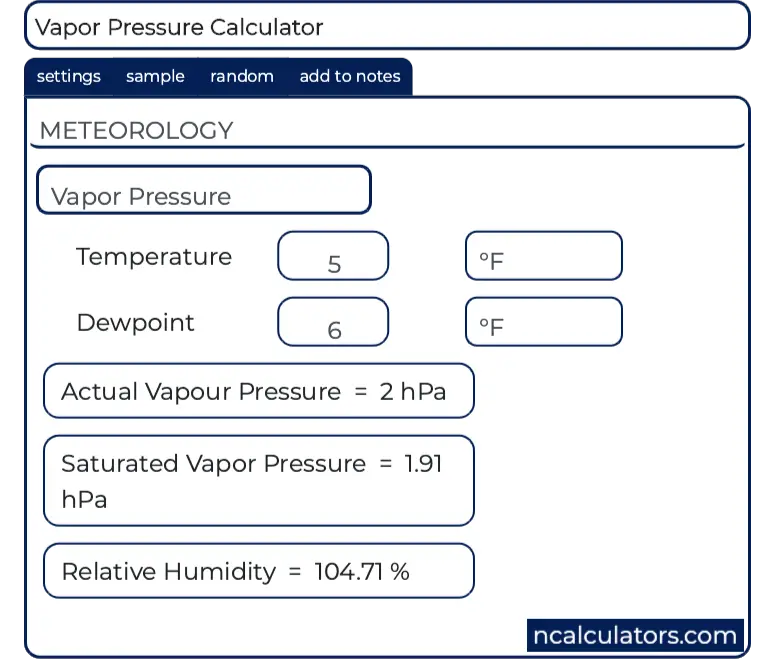
Relative humidity requires both temp and dewpoint. If you enter both the air temperature and the dewpoint you ll get a bonus answer. Mb in of hg mm hg hpa kpa lbs per square in.
If you want the actual vapor pressure enter the dewpoint. P d p p w where p is the entered ambient pressure and p w is the water vapor pressure. 2 p 226 3 pressure of dry air p d.

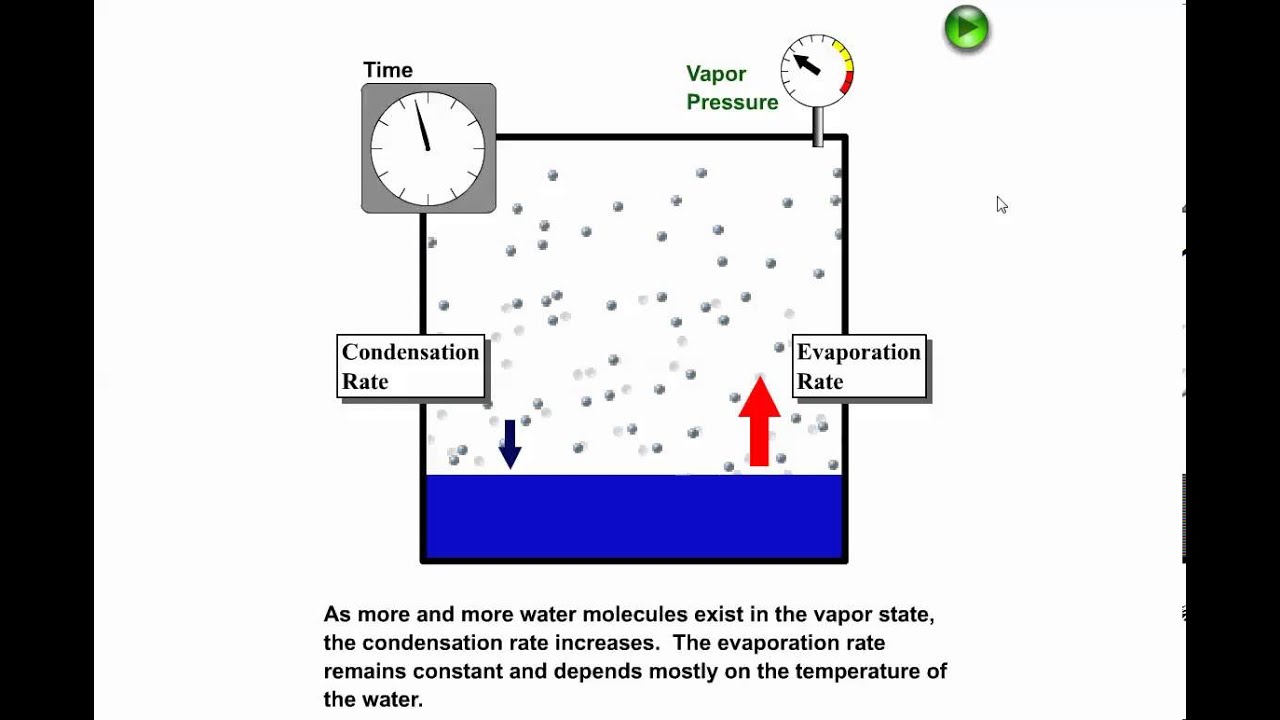
P w rh p ws 100 where p w is water vapor pressure rh is relative humidity p ws is saturated water vapor pressure. Water vapor pressure p w. If the amount of water in the air is just half of the saturation amount for example the relative humidity is 50 percent.

So relative humidity measures how much water the air currently contains as compared to what it would contain if saturated. In other words the actual vapor pressure is usually much lower than equilibrium vapor pressure. A higher percentage means that the air water mixture is more humid.

Relative humidity is normally expressed as a percentage. The relative humidity or of an air water mixture is defined as the ratio of the partial pressure of water vapor in the mixture to the equilibrium vapor pressure of water over a flat surface of pure water at a given temperature. The ideal relative humidity level is between 50 to 60 however the value becomes volatile based on the temperature.

It is often represented in percentage. Relative humidity often abbreviated as rh is the quantity which represents the amount of water vapor in the atmosphere or air. The rh is the amount of moisture in the air via moisture mass or vapor pressure divided by the maximum amount of moisture that could exist in the air at a specific temperature via max moisture mass or saturation vapor pressure.

Meteorologist jeff haby calculating the rh requires the correct equation s.
Relative humidity formula vapor pressure. Relative humidity rh is the ratio of the partial pressure of water vapor to the equilibrium vapor pressure of water at a given temperature. Relative humidity depends on temperature and the pressure of the system of interest. The same amount of water vapor results in higher relative humidity in cool air than warm air. Relative humidity the amount of water vapor in the air at any given time is usually less than that required to saturate the air.
The relative humidity is the percent of saturation humidity generally calculated in relation to saturated vapor density. The most common units for vapor density are gm m 3 for example if the actual vapor density is 10 g m 3 at 20 c compared to the saturation vapor. Relative humidity and vapor pressure. From the table above the saturation pressure at 70 o f 21 o c is 25 0 mbar.
If the vapor pressure in the actual air is 10 3 mbar the relative humidity can be calculated as. Humidity calculator solving for actual vapor pressure given relative humidity and saturated vapor pressure. Change equation select to solve for a different unknown. Solve for actual vapor pressure.
Solve for saturated vapor pressure. Dew point relative humidity. Reference books.

Reference books. Dew point relative humidity. Solve for saturated vapor pressure.

Solve for actual vapor pressure. Change equation select to solve for a different unknown. Humidity calculator solving for actual vapor pressure given relative humidity and saturated vapor pressure.

If the vapor pressure in the actual air is 10 3 mbar the relative humidity can be calculated as. From the table above the saturation pressure at 70 o f 21 o c is 25 0 mbar. Relative humidity and vapor pressure.
The most common units for vapor density are gm m 3 for example if the actual vapor density is 10 g m 3 at 20 c compared to the saturation vapor. The relative humidity is the percent of saturation humidity generally calculated in relation to saturated vapor density. Relative humidity the amount of water vapor in the air at any given time is usually less than that required to saturate the air.

The same amount of water vapor results in higher relative humidity in cool air than warm air. Relative humidity depends on temperature and the pressure of the system of interest. Relative humidity rh is the ratio of the partial pressure of water vapor to the equilibrium vapor pressure of water at a given temperature.