P total p b 0 p a 0 p b 0 x a. For example the equation can also be written as. Total vapour pressure relies on mole fraction of any one of the component that is either a or b.
Following conclusions are observed from the following relation. Conclusions on vapour pressure relation in liquid liquid solutions. According to the general definition those properties of a solution that depend on the number of solute molecules irrespective of their nature with respect to the total number of molecules present in the solution are.

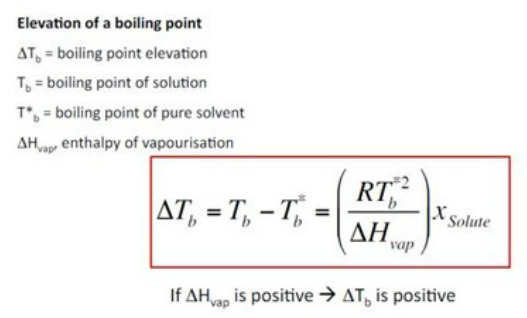
Relative lowering of vapour pressure let us first discuss the meaning of colligative properties. The boiling point is defined as the temperature at which the vapor pressure of a liquid equals the atmospheric pressure. Boiling point elevation is a colligative property related to vapor pressure lowering.

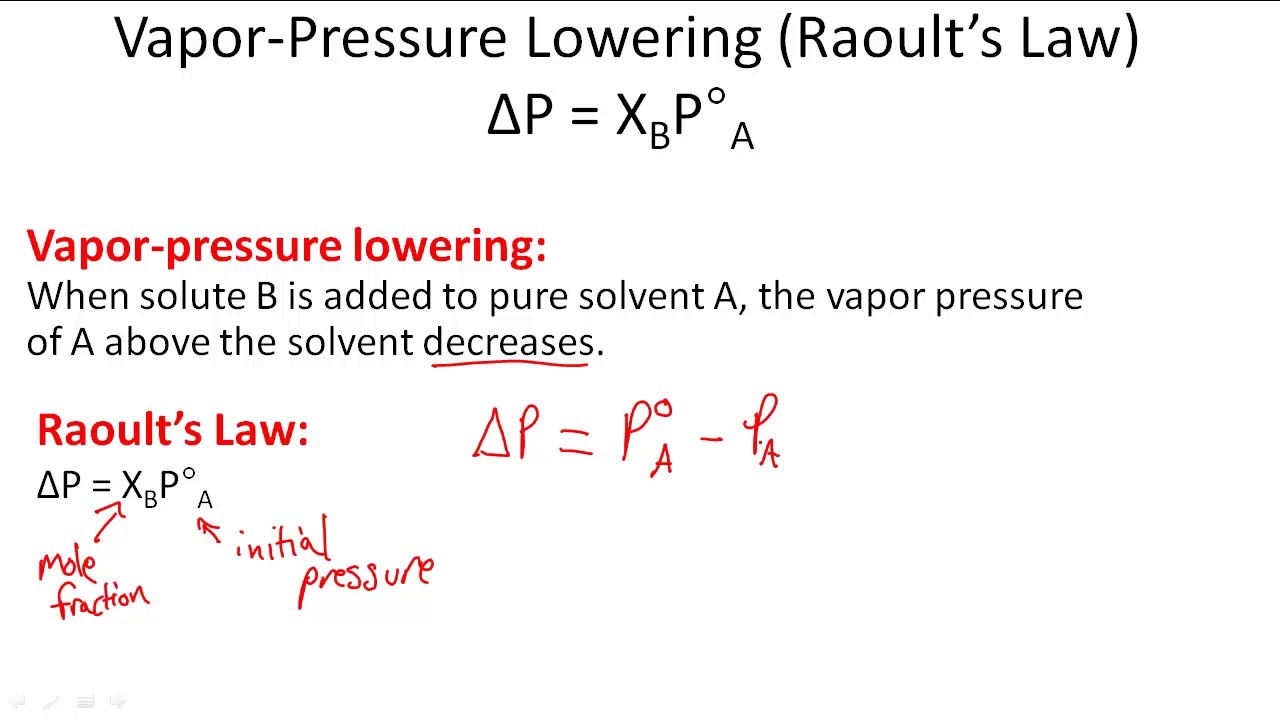
The equation that describes that phenomenon is called raoult s law. Therefore vapor pressure lowering is a colligative property. This small set of properties is of central importance to many natural phenomena and technological applications as will be described in this module.
These colligative properties include vapor pressure lowering boiling point elevation freezing point depression and osmotic pressure. As with the other colligative properties this equation is a consequence of the equality of solvent chemical potentials of the two phases in equilibrium. The osmotic pressure is proportional to the concentration of solute particles ci and is therefore a colligative property.

Examples of colligative properties include vapor pressure lowering freezing point depression osmotic pressure and boiling point elevation for example adding a pinch of salt to a cup of water makes the water freeze at a lower temperature than it normally would boil at a higher temperature have a lower vapor pressure and changes its osmotic pressure. But the vapor pressure of a solvent is not a colligative property. P c solvent p o.

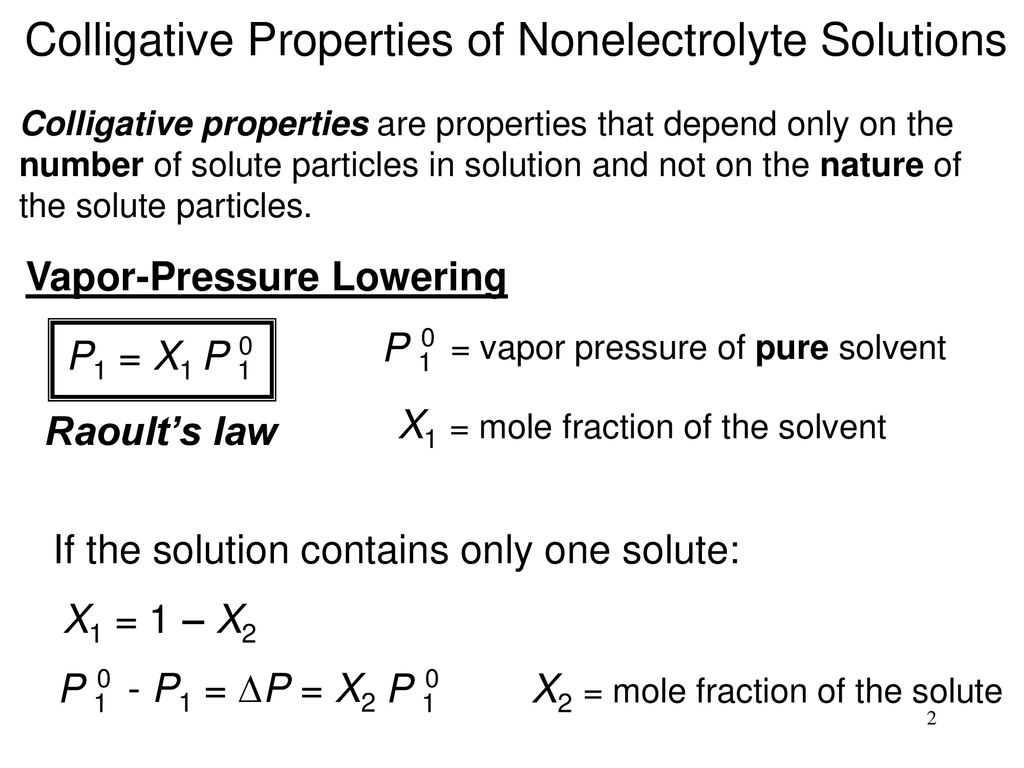
Raoult found that the vapor pressure of the solvent escaping from a solution is proportional to the mole fraction of the solvent.
Colligative properties vapor pressure formula. Vapor pressure over a solution. The vapor pressure over a pure liquid was covered in section 11 6 and described by the clausius claperyron equation when you add a solute to a pure liquid it becomes the solvent and the solute effect depends on whether the solute is volatile or nonvolatile. Colligative properties of solutions are properties that depend upon the concentration of solute molecules or ions but not upon the identity of the solute. Colligative properties include vapor pressure lowering boiling point elevation freezing point depression and osmotic pressure.
Lowering the vapor pressure. Measurement of colligative properties for a dilute solution of a non ionized solute such as urea or glucose in water or another solvent can lead to determinations of relative molar masses both for small molecules and for polymers which cannot be studied by other means. The best way to demonstrate the importance of colligative properties is to examine the consequences of raoult s law.

The best way to demonstrate the importance of colligative properties is to examine the consequences of raoult s law. Measurement of colligative properties for a dilute solution of a non ionized solute such as urea or glucose in water or another solvent can lead to determinations of relative molar masses both for small molecules and for polymers which cannot be studied by other means. Lowering the vapor pressure.

Colligative properties include vapor pressure lowering boiling point elevation freezing point depression and osmotic pressure. Colligative properties of solutions are properties that depend upon the concentration of solute molecules or ions but not upon the identity of the solute. The vapor pressure over a pure liquid was covered in section 11 6 and described by the clausius claperyron equation when you add a solute to a pure liquid it becomes the solvent and the solute effect depends on whether the solute is volatile or nonvolatile.

Vapor pressure over a solution.