Suppose a non volatile solute is now added to this pure liquid. Now let us take an example of a pure liquid the surface of the liquid is occupied by the molecules of the liquid. Vapour pressure is the pressure exerted by the vapours over the liquid under the equilibrium conditions at a given temperature.

Relative lowering of vapour pressure. Definition formula and exercises examples of vapor pressure lowering in everyday life is on a floating pool in tourist destination that adopts the trait of dead sea that makes you float when swimming. Vapor pressure lowering definition in chemistry and example.

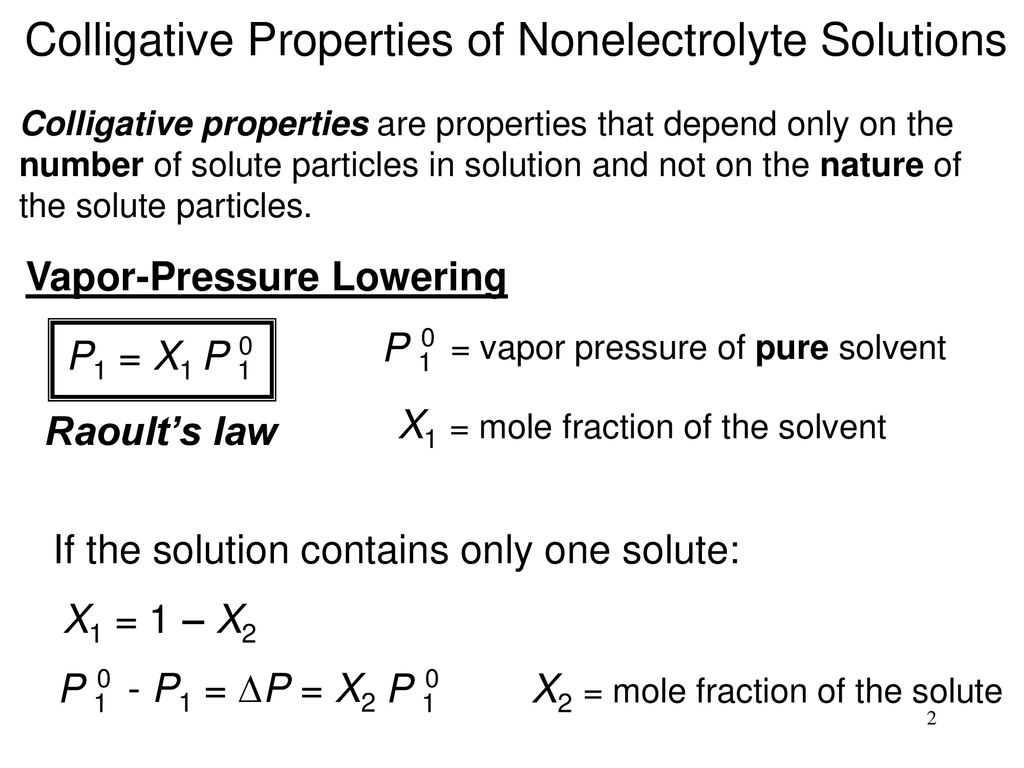
Recall that the vapor pressure of a liquid is determined by how easily its molecules are able to escape the surface of the liquid and enter the gaseous phase. A colligative property is a property of a solution that depends only on the number of solute particles dissolved in the solution and not on their identity. This is the formula you ll use to solve the most common sorts of vapor pressure problems you ll find in physics and chemistry classes.
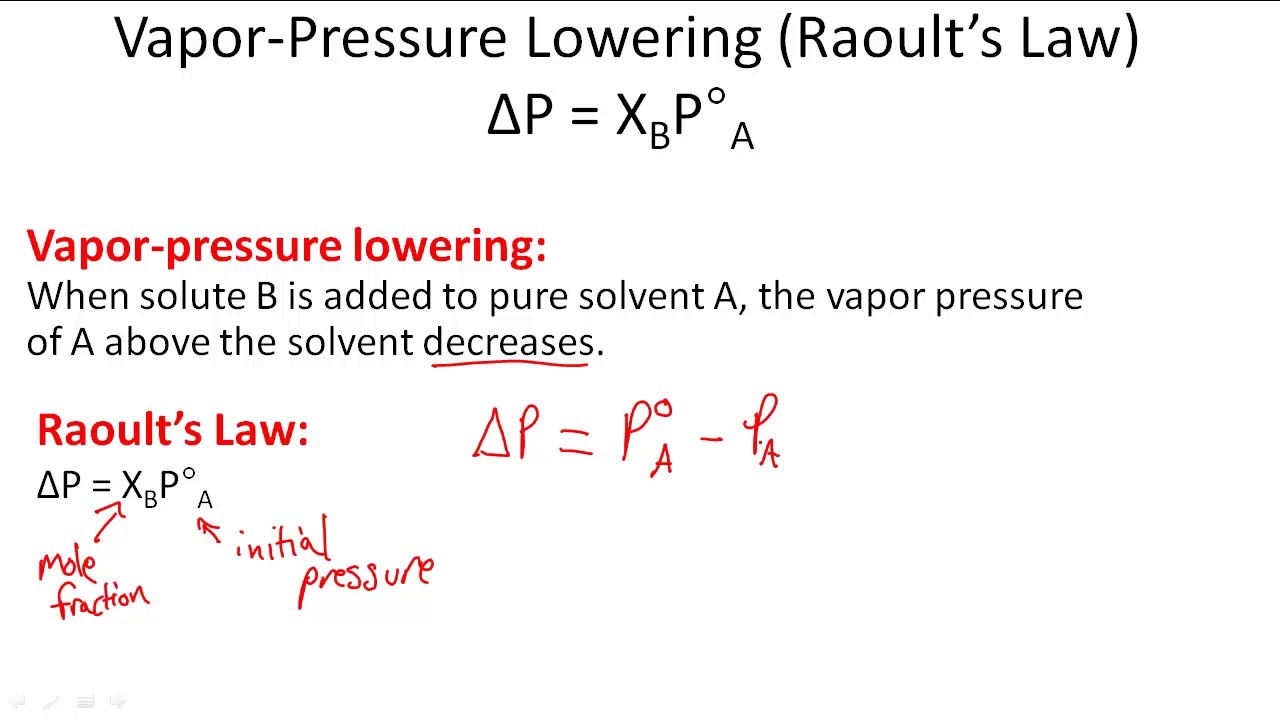
The formula used for calculating vapor pressure given a change in the vapor pressure over time is known as the clausius clapeyron equation named for physicists rudolf clausius and benoît paul émile clapeyron. Write the clausius clapeyron equation. When a solute is added to a solvent the vapor pressure of the solvent above the resulting solution is lower than the vapor pressure above the pure solvent.

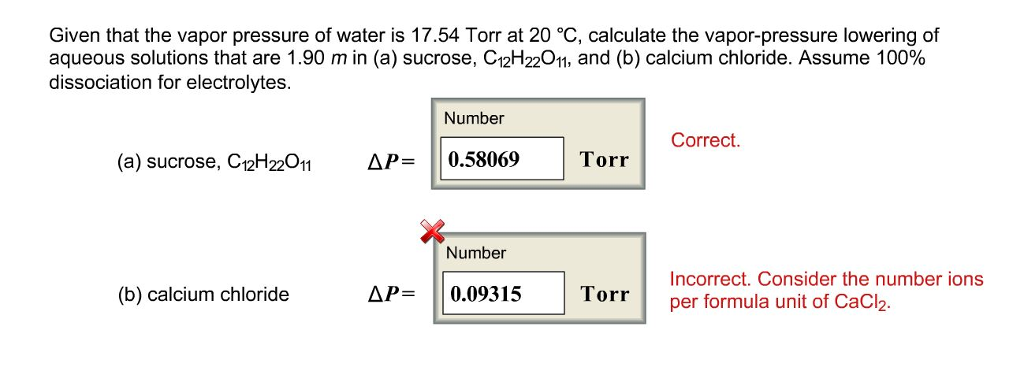
Click here to review vapor pressure of pure liquids and solids. In order to solve for raoult s law the mole fraction of water must be obtained. The vapor pressure of pure water at 25 c is 23 8 torr answer.

What is the vapor pressure of a solution at 25 c containing 3 5 moles of glucose in 10 0 moles of water. Vapor pressure formula questions. Similarly this vapor pressure lowering formula inner is no longer a form of contentless or unscheduled spontaneous activity and the content and regulation of the activity are no longer in the.

It relates to the tendency of particles to.
Vapor pressure lowering formula. At 25 o c the vapor pressure of pure benzene is 93 9 torr. When a non volatile solvent is dissolved in benzene the vapor pressure of benzene is lowered to 91 5 torr. What is the concentration of the solute and the solvent expressed in mole fraction. Vapor pressure lowering delta p 2 4.
Torr with chi solute 0 026. We need two pieces of information to calculate the reduction of the vapor pressure of the solvent in a solution containing a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte. The mole fraction of the nonvolatile solute x solute in the solution. The vapor pressure of the pure solvent p o solv.
Vapor pressure or vapour pressure in british english. See spelling differences or equilibrium vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases solid or liquid at a given temperature in a closed system the equilibrium vapor pressure is an indication of a liquid s evaporation rate.

See spelling differences or equilibrium vapor pressure is defined as the pressure exerted by a vapor in thermodynamic equilibrium with its condensed phases solid or liquid at a given temperature in a closed system the equilibrium vapor pressure is an indication of a liquid s evaporation rate. Vapor pressure or vapour pressure in british english. The vapor pressure of the pure solvent p o solv.

The mole fraction of the nonvolatile solute x solute in the solution. We need two pieces of information to calculate the reduction of the vapor pressure of the solvent in a solution containing a nonvolatile nonelectrolyte. Torr with chi solute 0 026.

Vapor pressure lowering delta p 2 4. What is the concentration of the solute and the solvent expressed in mole fraction. When a non volatile solvent is dissolved in benzene the vapor pressure of benzene is lowered to 91 5 torr.

At 25 o c the vapor pressure of pure benzene is 93 9 torr.